DERMOID CYST
Symptoms and Treatment

Dr. Surya Agarwal &
Dr. Deepak Goenka
Ovarian cysts are common, but often misunderstood, a condition that can cause pain and concern for women. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in the ovaries. They’re quite common and girls and women of any age can get them.
Most ovarian cysts don’t cause any symptoms and they’re usually benign (non-cancerous). Many go away without treatment or with medicines, but sometimes an ovarian cyst needs to be removed by surgery.
Dermoid cysts are rare and seen among 20% of abnormal ovarian growths.
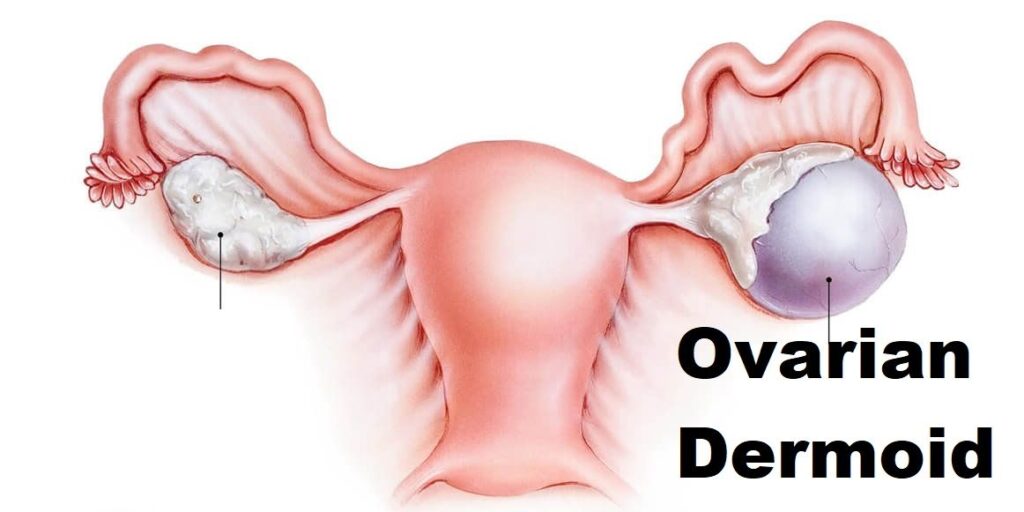
Dermoid cysts originate from totipotent germ cells (which are present at birth) that differentiate abnormally; developing characteristics of mature dermal cells. It is usually benign (98%) (Non-cancerous), which typically contains a diversity of tissues including hair, teeth, bone, thyroid, etc. They are also known as Benign Cystic Teratoma or Teratomas
It may occur at any age but the prime age of detection is in the childbearing (reproductive) years [16-55 yrs.]. The average age is 30 years. Up to 15% of women with ovarian teratomas (dermoid cyst) have them in both ovaries. Dermoid cysts can range in size from a centimeter (less than a half-inch) up to 45 cm (about 17 inches) in diameter.
Most frequently found incidentally during physical or radiographic examinations for other reasons. Although an imaging test, usually a pelvic ultrasound (USG), is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are also sometimes used, but less commonly.
The symptoms, when present, include:
- pain or discomfort in your lower abdomen (tummy)
- pain during sex
- back pain
- need to pass urine more often or urgently
- find it more difficult to poo or feel pressure in your back
- the passage that makes you feel you need to go to the toilet feel bloated
- get indigestion or heartburn or feel very full after you eat
- painful periods or a change in the pattern of your periods
These cysts can cause the ovary to twist (torsion) and imperil its blood supply, which usually produces acute and severe pain. It is an emergency and calls for urgent surgery. The larger the dermoid cyst, the greater the risk of rupture with spillage of the greasy contents which can create problems with adhesions, pain and infections.
In most of the cases, complete removal of the ovary (ovariotomy) is not required. Removal of the dermoid cyst (cystectomy) is usually the treatment of choice. This is usually done Laparoscopically (rarely requires Laparotomy / open surgery).


Excelplent pst but I wass wanting to khow if yyou coulpd wriute a littee more
on tgis topic? I’d bee veery grateful if youu could
elabordate a little bit further. Cheers!
Kindly e-mail me at info@ihrindia.com what exactly you want to know, we will be happy to help you.
Great article! Very informative and easy to understand. Thanks for explaining the symptoms and treatment options for dermoid cysts so clearly.