Trusted by thousands of couples for compassionate care and successful outcomes
At the Institute of Human Reproduction (IHR) Guwahati, we understand that every fertility journey is personal, emotional, and life-changing. IVF brings together medical science and hope, and we are proud to be one of the leading fertility centres in India, offering world-class IVF success rates.
The success of IVF is influenced by several important factors, including:








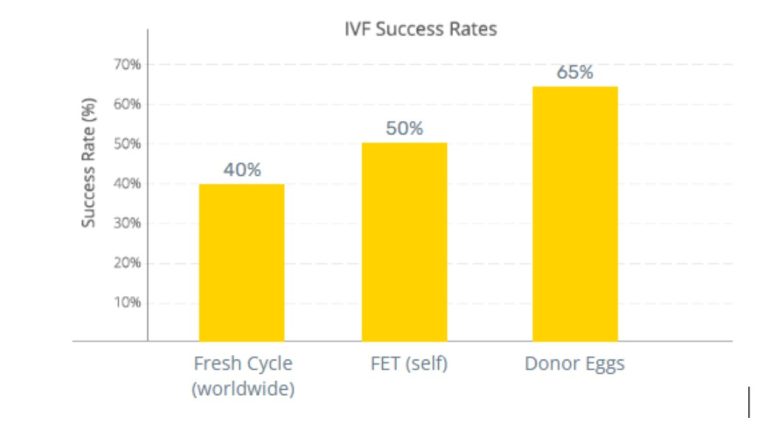
While average global IVF success rates for fresh cycles range between 35% to 45%, we at IHR are consistently delivering higher success due to our scientific approach, focus on patient care, and advanced procedures.
Here’s what you need to know:
1. Fresh (same) Cycle Transfer
In a fresh cycle, the best-quality embryos are transferred into the uterus three to five days after the egg retrieval, all within the same cycle. Any extra viable embryos are frozen and stored for future use.
Advantages:
However, in some cases, the hormonal stimulation used during egg retrieval can affect the uterine lining, which may slightly lower the chances of successful implantation.
2. Frozen Embryo Transfer
In a Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET), all embryos — including the best quality ones — are frozen immediately after fertilization. These embryos are later thawed and transferred into the uterus in a subsequent cycle, either the next month or later, based on the patient’s condition and readiness.
FET is typically performed after a gap from ovarian stimulation, allowing the woman’s hormone levels to return to normal, which closely mimics a natural conception environment. This balance has shown to positively influence both embryo implantation and the health of the baby.
Study shows that increasing the time between administering the drugs and pregnancy lowers the chances of a woman’s risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS).
FET allows clinicians to be more flexible and use drugs which lowers the risk of OHSS to almost nil. We are proud that IHR is an OHSS free clinic.
Also, the live birth rate per transfer is higher with FET when compared to Fresh Cycle Transfer.
Advantages:
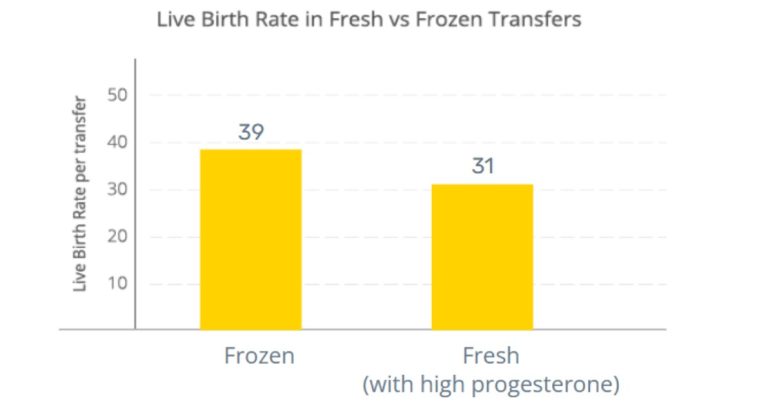
Positives and Negatives of Frozen and Fresh Transfer
Data shows that the success rate is higher if a couple undergoes FET
Source: Fertstert

A donor egg (also called egg donation) refers to the process in which a woman donates her eggs (oocytes) for another person or couple to use in assisted reproductive technology (ART), most commonly in vitro fertilization (IVF). This allows people who cannot use their own eggs to conceive — such as women with low ovarian reserve, premature ovarian failure, advanced maternal age, or certain genetic conditions — to have a baby.
The First (Single) attempt is between 50% to 65% depending on the type of IVF treatment done. We are able to consistently maintain this success rate because of due diligence and the high standard which we have set for ourselves. We also focus more on FET as data suggests its benefits.
IVF success rates improve with multiple attempts. The chance of a couple conceiving in three attempts is around 90%.
Pre-implantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT may be useful in elderly patients or patients with poor AMH (Anti-Mullerian Hormone) who want to try IVF with their own eggs, also used in patients with a history of a genetic disorder, recurrent pregnancy loss.
Endometrial Receptivity Analysis (ERA)
Performed using a biopsy of the uterine lining for testing its receptivity for embryos on the day of the transfer. Done selectively in cases of recurrent IVF failure.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy – both diagnostic as well as therapeutic done before IVF to detect Uterine defects and to confirm the site for embryo transfer(Trial ET).
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
A single sperm is inserted into the ovum using specialized equipment, done for the cases of very very low sperm count or previous history of poor fertilization or in case of PGT.
Platelets Rich Plasma (PRP)
PRP can be either Endometrial PRP or Ovarian PRP. It is extracted from patients’ blood and is injected into the endometrium for cases of thin endometrium to improve endometrial lining or it may be injected into the ovary to improve ovarian functions in elderly patients or patients with poor AMH (Anti-Mullerian Hormone).
Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting (MACS)
MACS is an advanced semen preparation technique, that may help in cases of recurrent IVF failures or patients with high DFI (DNA Fragmentation Index)
Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH)
A small crack in the outer coating of the embryo(zona) Is made with the help of a laser to assist embryo hatching and implantation and may be helpful in cases of recurrent IVF failures after Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)
Embryo Glue
Embryo Glue is a specialized transfer medium enriched with hyaluronan that helps enhance embryo attachment to the uterine lining. It is used during embryo transfer to improve implantation rates and may be particularly beneficial for patients with previous IVF failures or poor implantation history.

Copyright 2025 © IHR Guwahati. All Right Reserved.