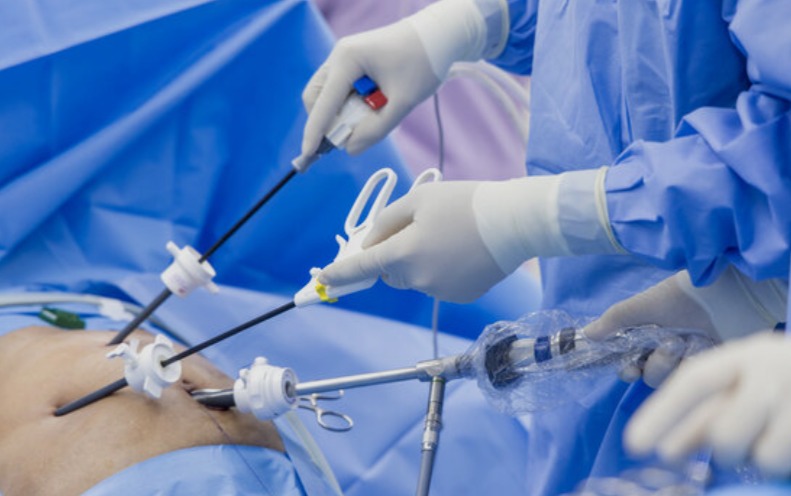
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS), Keyhole Surgery, or Band-Aid Surgery, is a modern surgical technique where operations are performed through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.0 cm) instead of large open cuts. This technique allows surgeons to access organs within the abdomen or pelvis using a laparoscope – a small tube with a camera and light – to view internal structures on a monitor.
At IHR Guwahati, we are proud to offer advanced laparoscopic surgeries performed by skilled and experienced surgeons using state-of-the-art technology. We ensure faster recovery, minimal discomfort, and superior outcomes.
Our specialists use laparoscopy to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions, including:

There are several advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an open procedure.
These include:
While laparoscopy is generally safe, potential risks include:
Our surgeons follow rigorous safety protocols and individual risk assessment for every patient.
In-Hospital
At Home Care
Sexual Activity:
Generally safe to resume after 7 days, following clearance from your surgeon.
Most patients recover within 3–7 days, depending on the type and complexity of the surgery. You can typically resume light activities within a few days.
Laparoscopy is significantly less painful than open surgery. Mild discomfort or soreness may be felt for a couple of days, which can be managed with prescribed painkillers.
The incisions made are very small, and most patients have minimal scarring, if any. Cosmetic appearance is significantly better than traditional open surgery.
Yes. It is commonly used to diagnose and treat fertility issues such as blocked fallopian tubes, endometriosis, or ovarian cysts.
While laparoscopy is safe for most patients, those with specific medical conditions, multiple prior surgeries, or obesity may require special evaluation before proceeding.

Copyright 2025 © IHR Guwahati. All Right Reserved.